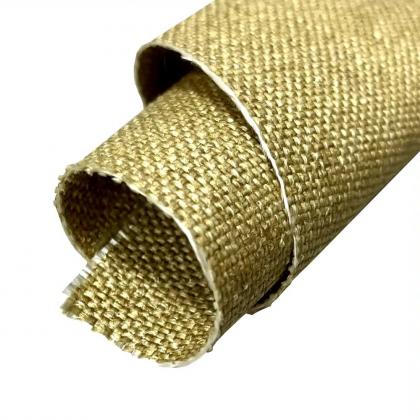
- Силиконовая стекловолоконная ткань с покрытием
- Сварка стекловолокна.
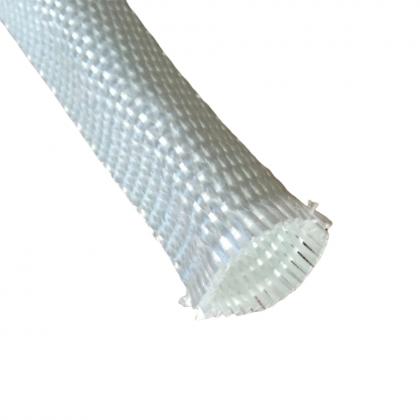
- Защитник из нейлонового рукава
- Гидравлический шланговый рукав
- Нейлоновая защитная рукав для шланга
- Гидравлический шланг защитный огневой рукав
- огневой рукав для шланга
- защитный огневой рукав шланга
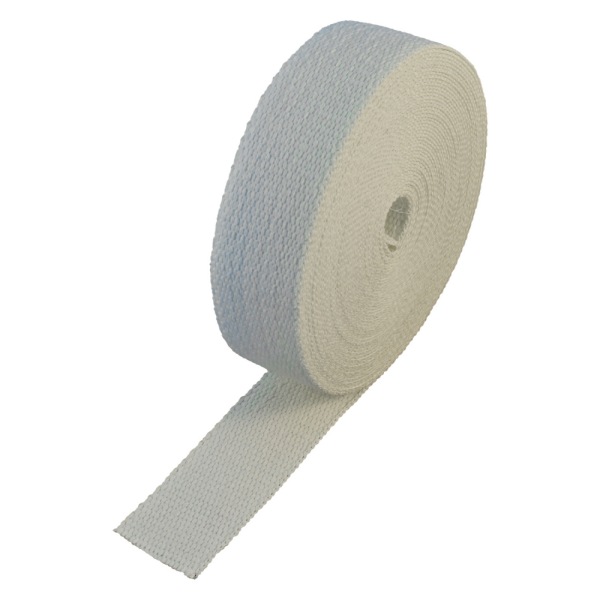
- керамическая лента волокна
- Игла из стекловолокна с алюминиевой фольгой
- NINGGUO BST THERMAL PRODUCTS CO., LTD.
- Отправить нам: vanessa-cheng@live.cn
- Позвони нам: +86 15856303740
















 Specated Ipv6 Network
Specated Ipv6 Network 